Common Uses of Compressed Air in the Manufacturing Industry

Compressed air is a vital utility across the manufacturing industry. Known as the “fourth utility” alongside water, electricity, and natural gas, compressed air is essential in driving equipment, ensuring product quality, and improving operational efficiency. This critical resource supports many manufacturing applications, enabling businesses to meet production demands while maintaining precision and reliability.
This article will explore common uses of compressed air in the manufacturing industry, highlighting how this versatile energy source supports various functions, including powering tools, managing materials, and facilitating safety features.
Powering Pneumatic Tools
One of the most significant applications of compressed air in manufacturing is its ability to power pneumatic tools. These tools are widely used because they are lightweight, efficient, and reliable compared to their electric counterparts. From drills and sanders to wrenches and hammers, pneumatic tools are essential for assembly lines that require consistent power and precision.
Compressed air systems ensure that these tools operate effectively, reducing downtime and improving overall productivity. For instance, manufacturing lines producing automotive components often rely on pneumatic tools for tasks requiring accuracy and consistency. This makes compressed air indispensable for sustaining productivity in environments where reliability is paramount.
Additionally, pneumatic tools powered by compressed air contribute to worker safety. With fewer moving parts than electric tools, they are less prone to overheating and failure, decreasing the risk of workplace accidents. This combination of performance and safety makes compressed air systems foundational to manufacturing operations.
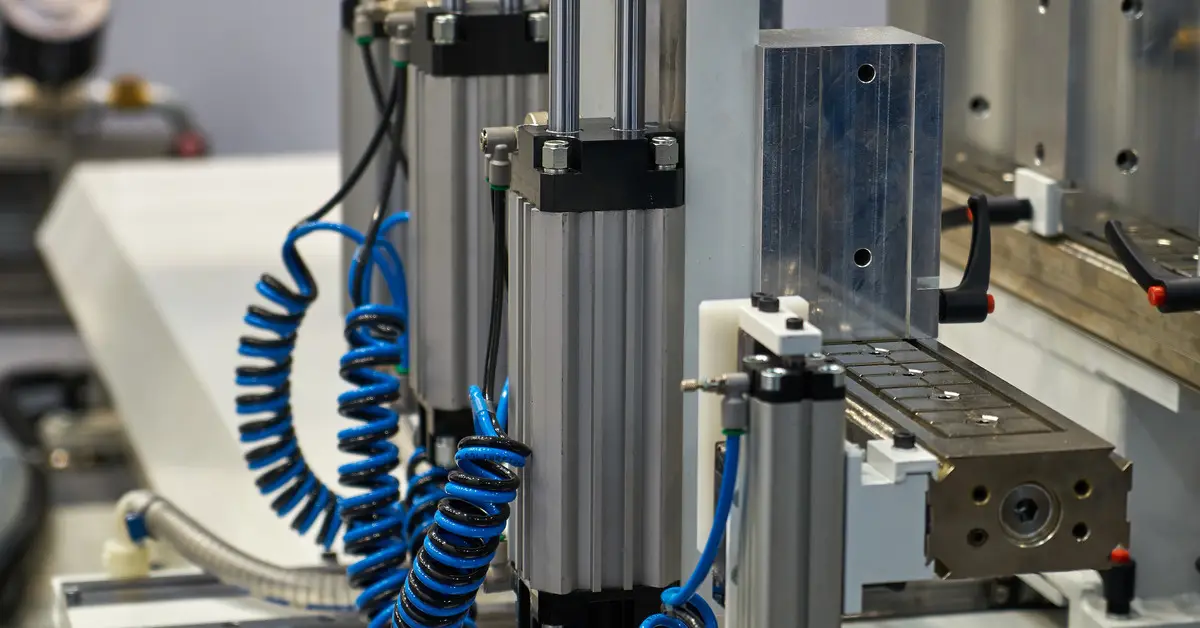

Material Handling Systems
Material handling is another critical area in which compressed air demonstrates its versatility and importance in the manufacturing sector. Compressed air powers vacuum systems and conveyor belts used for transporting raw materials and finished products. These systems are particularly useful in facilities working with fragile materials that require careful handling.
Vacuum systems using compressed air can create suction to lift and transport materials such as glass panels, electronic components, and food products. This minimizes the risk of damage and maintains product integrity, reducing waste and maintaining high production standards.
Compressed air also supports conveyor belt systems, ensuring smooth operation and efficient product movement. By relying on compressed air, manufacturers can achieve consistent and seamless material handling in even the most demanding environments.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Compressed air is essential in cleaning and maintaining equipment and facilities throughout the manufacturing industry. Dust, debris, and other contaminants can accumulate on machinery and work surfaces, potentially causing equipment malfunctions or product defects over time. Using compressed air for cleaning ensures that parts remain in optimal condition, ultimately extending their lifespan and ensuring uninterrupted production.
For example, factories can use compressed air to clear out tight spaces and hard-to-reach areas prone to dirt and residue buildup. This makes maintenance tasks more efficient while reducing the risk of contamination in sensitive manufacturing processes, such as food packaging or pharmaceuticals.
Furthermore, compressed air contributes to maintaining indoor air quality within manufacturing facilities. By integrating tools, such as a refrigerated air dryer, businesses can remove moisture from compressed air systems, reducing the risk of condensation and ensuring high-quality, dry air for operations.
Enhancing Industrial Automation
The rise of industrial automation in manufacturing has further increased the reliance on compressed air systems. Automation requires precise, consistent control of tools and machinery, which compressed air can provide. Actuators, cylinders, and other pneumatic components rely on compressed air to execute automated processes efficiently and reliably.
For example, robotics used in assembly lines often depend on compressed air for movement and positioning. These systems require consistent air pressure to operate accurately, ensuring that automated processes function smoothly without delay. This highlights the essential role of compressed air in modern manufacturing processes, where precision and reliability are critical to success.
Compressed air also integrates seamlessly into programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and other control systems that manage automation. By powering automated components, compressed air helps manufacturers achieve greater efficiency and accuracy while reducing manual intervention, leading to cost savings and improved product quality.
Facilitating Product Quality
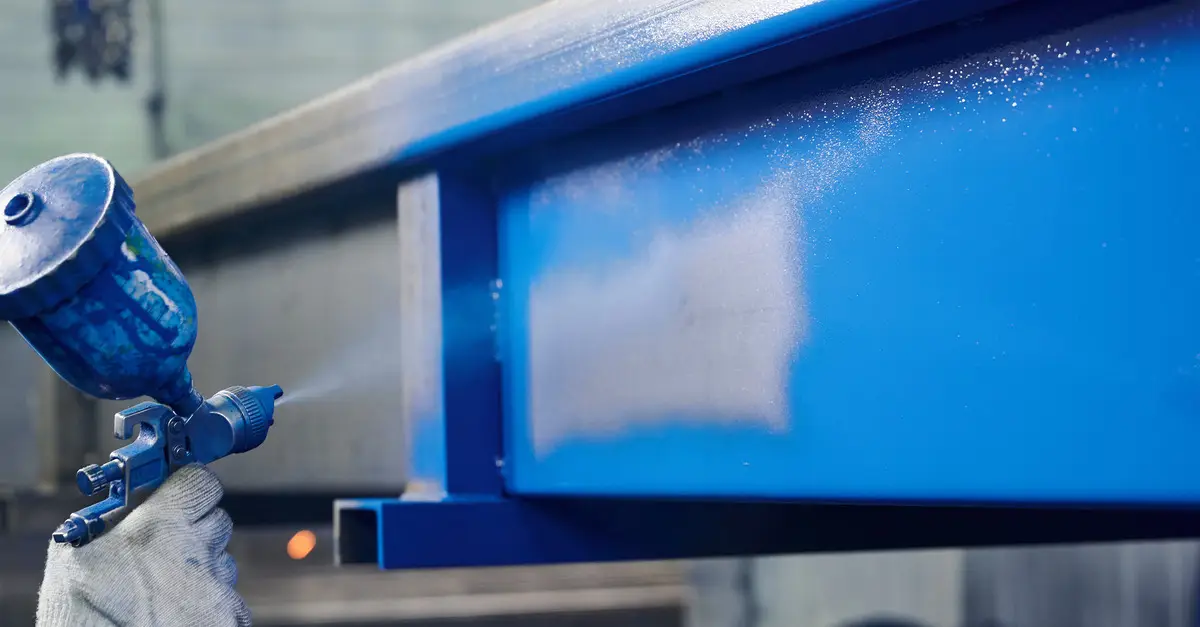
Compressed air aids in maintaining consistent product quality across multiple applications. This includes everything from spray painting and coating to packaging and product testing. Manufacturing processes that require precision and consistency rely heavily on compressed air to ensure that desired outcomes are consistently achieved.
For instance, spray painting systems use compressed air to distribute paint on various surfaces evenly, ensuring a uniform and smooth finish. This is especially critical for automotive and aerospace manufacturing industries, where product aesthetics are paramount.
Similarly, compressed air is used for filling and sealing equipment that packages consumer goods. The accuracy achieved through compressed air ensures that products meet stringent quality standards, whether packaging beverages or sealing pharmaceutical products.
Compressed air’s ability to provide precise control and power directly supports manufacturers in delivering reliable and high-quality products to market.

Supporting Safety Systems
Compressed air is also used to enhance safety within manufacturing environments. Compressed air contributes to safer workspaces across industries, from powering safety mechanisms to operating fire suppression systems.
Emergency systems powered by compressed air include air brakes for heavy machinery and pneumatic shutoff valves for hazardous material containment. These systems ensure rapid responses to potential safety risks, minimizing the risk of injury or damage.
Additionally, manufacturing facilities often rely on compressed air to operate fire suppression systems. These systems efficiently release water or chemical agents to extinguish flames, protecting both workers and valuable equipment.
The role of compressed air in maintaining safety cannot be overstated; it provides a reliable, fast-acting solution for addressing risks in high-stakes manufacturing environments.
Cost and Energy Efficiency Benefits
Another significant advantage of compressed air systems in manufacturing is their contribution to cost and energy efficiency. Compressed air allows manufacturers to combine multiple operations into a single system, eliminating the need for multiple energy sources. This centralized approach reduces equipment costs and energy use.
Modern compressed air systems are designed to be energy-efficient, with technologies that optimize air pressure, minimize leaks, and recover energy during operation. These improvements translate to lower energy bills and reduced environmental impact for manufacturers.
For instance, implementing variable speed compressors enables manufacturers to adjust air pressure based on demand, avoiding unnecessary energy consumption during low-use periods. Additionally, by investing in newer, more efficient systems, businesses can achieve significant cost savings over time while minimizing their carbon footprint.
Unlocking the Potential of Compressed Air
These common uses of compressed air in the manufacturing industry demonstrate its crucial role in supporting operational efficiency, safety, and product quality. Compressed air remains an irreplaceable resource across diverse applications, from powering pneumatic tools to enabling industrial automation.
By integrating advanced technologies such as refrigerated air dryers and energy-efficient compressors, manufacturers can further enhance the performance and reliability of their compressed air systems. This enables businesses to maintain a competitive edge while meeting evolving industry standards.
Adopting and maintaining high-quality compressed air systems is an investment that ensures long-term success in the manufacturing industry. Compressed air is undeniably one of the most valuable tools for manufacturers looking to optimize their operations.