A Guide for Maintaining Air Compressors

Regularly maintaining industrial air compressors achieves dependable performance and avoids costly breakdowns. This guide for maintaining air compressors provides an overview of the precise actions, intervals, and best practices that keep air compressors operating efficiently. Readers will gain a clear understanding of essential preventive care techniques, signs of impending issues, recommended schedules, and specific approaches that maximize equipment lifespan. After reading, you will have practical knowledge you can apply to make maintenance hassle-free, safe, and reliably effective.
Why Maintenance Matters
Air compressors are the heartbeat of production facilities, workshops, and a range of commercial operations. Their reliable operation supports essential processes such as powering pneumatic tools, packaging systems, and spray painting. Downtime leads to disruptions, lost revenue, and added expenses.
Well-maintained air compressors operate optimally, use less energy, require fewer major repairs, and deliver a safer workplace. Lack of proper upkeep causes excess wear, increased operating temperatures, declining air quality, and even catastrophic failure.
Most manufacturers require proof of regular service to maintain warranty coverage. Commitment to maintenance signals long-term reliability, predictability of costs, and customer satisfaction.
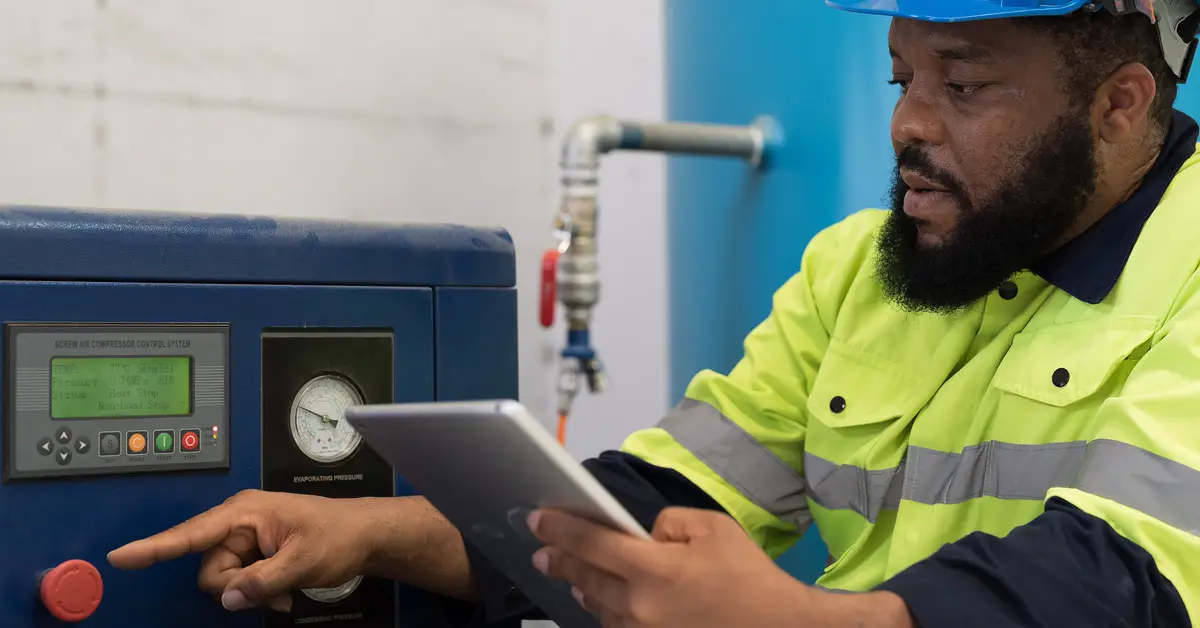

Understanding Air Compressor Components and Functions
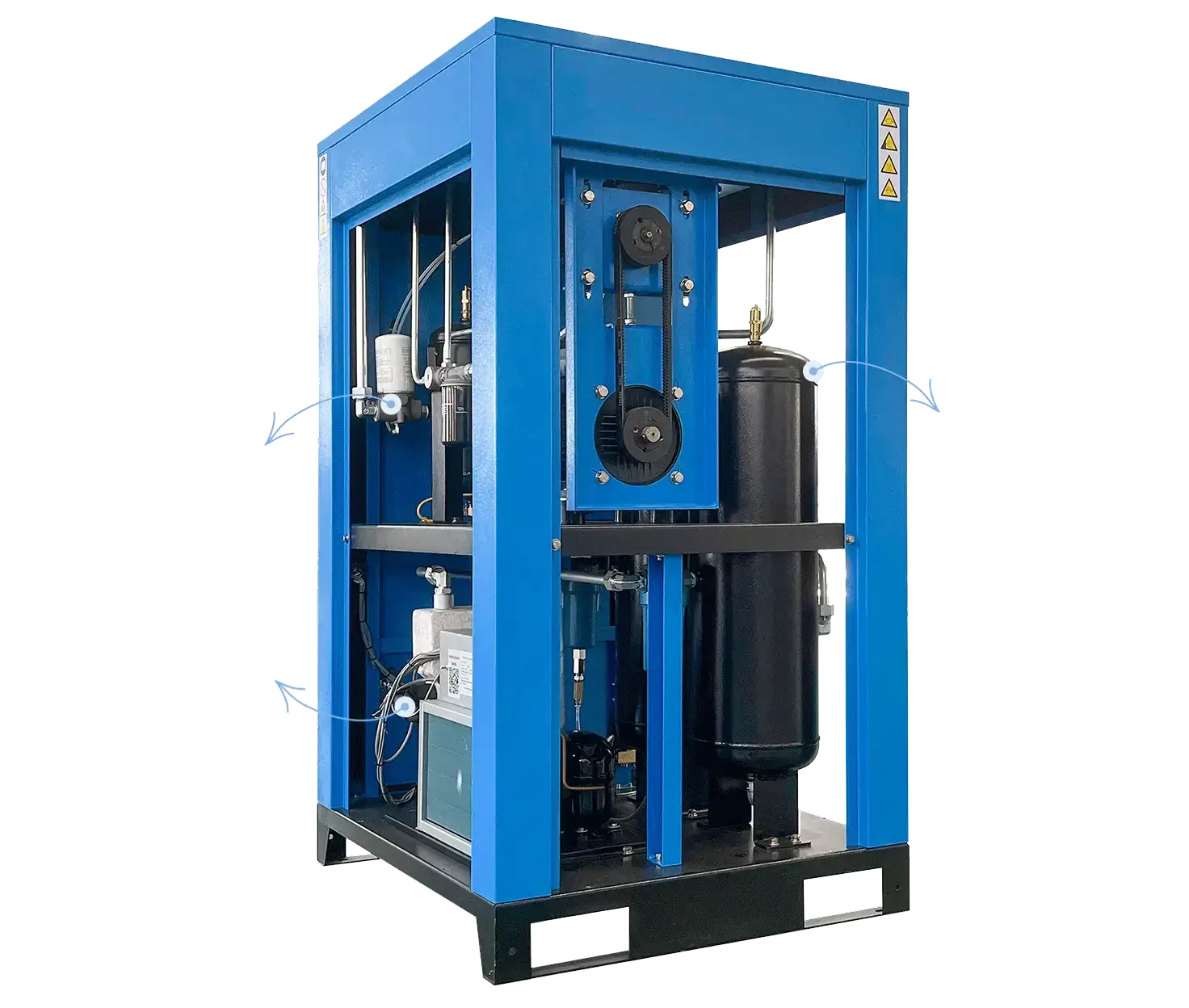
Effective maintenance requires an in-depth understanding of the core systems within industrial air compressors. Most units, including fixed-speed rotary screw compressors and reciprocating models, share major components but differ in complexity and output.
The primary systems requiring attention include the compressor pump, intake air filter, oil system, belts, motor, cooling system, and electrical components. Each part operates under significant mechanical and thermal stress throughout daily operations.
Lubrication systems need periodic checking, as their role in protecting internals from friction and heat is fundamental. Filters ensure that contaminants are not pulled into critical parts or introduced to the compressed air supply, preserving equipment and product quality. Belts and couplings demand correct alignment and tension for smooth power transfer.
Intake filters, separator elements, drains, pressure switches, and safety valves all protect assets and personnel. Electrical panels, gauge assemblies, and wiring must be secure and clear of dust or moisture. Understanding the responsibilities of each element supports the establishment of a reliable maintenance routine.
The Importance of a Routine Maintenance Schedule
Air compressors operate best with proactive, scheduled maintenance. Every manufacturer provides a schedule tailored to their models and common duty cycles. Strict adherence to these intervals keeps warranties intact, supports efficient operation, and prevents unexpected interruptions.
Commit to regular attention for items like oil changes, filter replacements, inspections, and system cleanings. Review hours of operation to determine correct intervals. Consider increasing the frequency of certain service tasks for facilities running compressors in harsh environments or on extended duty cycles. Using high-quality, manufacturer-approved oils and replacement parts ensures optimal outcomes.
A detailed log tracks completed maintenance and provides helpful data for warranty claims, troubleshooting, and performance analysis. Whether working with a small portable unit or a large industrial fixed-speed rotary screw compressor, this discipline minimizes risk and maximizes uptime.
Daily Inspection and Preventive Tasks
Routine visual inspection remains a fundamental measure in reliable compressor care. Including a daily walkaround in your protocol can detect leaks, abnormal sounds, high temperatures, or unusual vibrations early. Address these warning signs promptly to avoid costly repairs or catastrophic failure.
Monitor all instrumentation to ensure the compressor operates within specified parameters. Check oil levels and notice any unusual consumption or discoloration. Confirm the cleanliness of intake areas and filters. Drain condensation from air receiver tanks and ensure that automatic drains function properly. Excess moisture or oil in the compressed air supply can damage both the compressor and the pneumatic tools it serves.
Carefully inspect hoses and connections for signs of wear, cracks, or looseness. Tighten, replace, or lubricate to maintain a sealed, efficient system. Safety equipment, including pressure relief valves and emergency shutdown switches, should be examined and tested frequently.
Weekly and Monthly Maintenance Essentials
Beyond daily checks, schedule weekly and monthly attention to foster reliability and ensure warranty protection. During weekly reviews, clean or replace intake filters if needed. Inspect drive belts, pulleys, and tensioners, adjusting alignment or tension as manufacturer specifications indicate.
Monitor cooling mechanisms and fans for dust buildup, blockages, or signs of degrading performance. Check and clean separator elements. Inspect electrical contacts and enclosures for moisture intrusion, corrosion, or inadequate insulation.
Perform a more comprehensive review of the lubrication system monthly. Change compressor oil when required, verifying the type and service interval match manufacturer recommendations. Contaminated or low-quality oil puts the entire system at risk. Some models require monthly cleaning or testing of condensate drains and traps, especially when environmental conditions are humid or watery byproducts are common.
Survey all warning labels and safety signage for visibility and legibility. Employees and operators must have immediate access to critical information during daily use and emergencies.
Quarterly and Annual Maintenance Procedures
Quarterly and annual service routines reflect the highest level of commitment to air compressor reliability, safety, and operational assurance. Complete a deep clean of the compressor’s exterior every three months, remove accumulated dust from the cooling fins, and check moving parts for alignment and lubrication. Conduct a thorough test of all electrical systems, tightening connections and replacing worn components as needed.
Annually, schedule overhauls to address components approaching end-of-life or requiring detailed service. Replace major elements like separator elements, worn drive belts, and high-cycle valves. Hire a qualified technician to conduct an air quality analysis and inspect the pressure vessel’s interior for corrosion, scaling, or signs of stress fractures.
Document every action performed, with supporting details and insights from each inspection. Yearly analysis supports compliance and the most generous warranties, reassuring you of long-term performance and lower total cost of ownership.
Building a Maintenance Culture
A commitment to maintenance starts with leadership but depends on buy-in from every stakeholder. Make maintenance procedures and schedules visible in your workspace. Invest in operator training and certifications to increase awareness of equipment care. Track performance metrics such as uptime, power consumption, and repair frequency to monitor the real benefits of proactive maintenance.
Communicate clearly about warranties, guarantees, and the tangible financial benefits of disciplined care. Building a maintenance culture protects not just your air compressor, but the productivity and safety of your entire operation. It reassures staff that they use high-quality, dependable equipment designed to support them over the long term.

Ensuring Long-Term Reliability
This guide for maintaining air compressors aims to instill confidence and clarity around the responsibilities of air compressor care. Reliable maintenance practices extend service life, deliver predictable operational costs, and qualify your assets for the most comprehensive warranties on the market.
Whether you manage complex production lines powered by large units or handle smaller fixed-speed rotary screw compressors, these recommendations offer lasting value and peace of mind. For any uncertainty, consult the manufacturer’s documentation or enlist professional support to guarantee that best practices are met without compromise.
Commit to maintenance, document every inspection, and foster a culture that values reliability above all. Doing so will ensure your operation never needs to worry about preventable compressor issues and that your investment remains protected and productive for years to come.